Extending Scratch
Why Scratch
Scratch2 is becoming more mature with a steadily growing user community. MIT has done a great job at propelling programming education.
We focus on how to leverage Scratch to further enable hardware interaction for the young.
The challenge is extending Scratch and make it talk to the various boards and devices.
But How?
Here is the architecture of the Scratch extension module. Note this is still under development by the Scratch team and is subject to change.
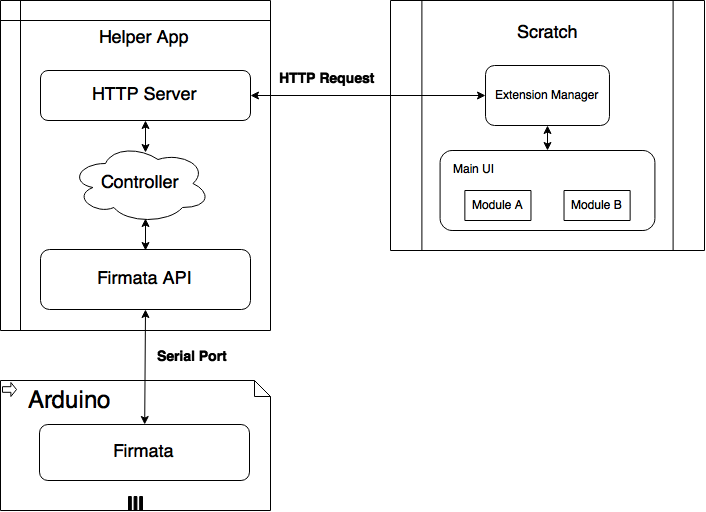
You can also check the official extension wiki to get the latest updated info.
What else?
As you can see in the architecture diagram, you will need a helper app to enable the communication as Scratch does not speak on channels other than the HTTP protocol.
What you need is a third party, preferrably open sourced project to do that. Your helper app should act as an HTTP proxy and talk to Scratch AND it should also be able to talk to the board via serial ports.
All the Help You Can Get
Let’s take a look at some open source initiatives
Both projct is based on the Firmata protocol.
johnny-five
This popular project is node-js based. Highly configurable, actively maintained and very popular. You can leverage the server module of the nodejs project and easily put together a helper app with very little code.
Some sample code:
var five = require("johnny-five");
var board = new five.Board();
board.on("ready", function() {
var led = new five.Led(13);
led.blink(500);
});s2a_fm
This project bases on PyMata, a firmata Python client. It already integrated the server request handling and Firmata communication. You can extend the existing modules within the framework relatively easily.
Here is a video for s2a_fm based project
You can choose whichever project you are comfortable with.
Final product
Please checkout DFRobot’s DF4Scratch. It combines all the stuff together and provides an easy way to access Arduino via Scratch. It can also control the Vortex robot.